Grafana
-
Kubernetes observability – log aggregation – Grafana-loki deployment and configuration
Table of Contents
Intro
This page describes how to deploy and apply basic configurations – including retention policies – to a promtail-loki stack.
Loki is a log storage solution tightly integrated with Grafana. It can ingest logs from multiple sources (in our case, containers), index them and makes them accessible via Grafana UI.
Its functionalities overlap with elasticsearch. Grafana-loki is more lightweight since it indexes only entries metadata and not the entire content of each log line.
Data can be pushed into loki with multiple solutions (e.g. promtail, fluent bit, fluentd, logstash, etc.). See https://grafana.com/docs/loki/latest/clients/
This page describes how to use promtail for such purpose.
The following setup is not meant to be used on production environments.
Requirements
- A k8s cluster including Grafana
- all appropriate configurations to use kubectl command line tool
Loki deployment
- Add loki helm chart repo
helm repo add grafana https://grafana.github.io/helm-charts helm repo update
- Create a file values.yaml to store all chart settings that must be overridden from the default values
loki: commonConfig: replication_factor: 1 storage: type: 'filesystem' compactor: working_directory: /var/loki/data/retention shared_store: filesystem compaction_interval: 10m retention_enabled: true retention_delete_delay: 2h retention_delete_worker_count: 150 schema_config: configs: - from: "2022-12-01" index: period: 24h prefix: loki_index_ object_store: filesystem schema: v11 store: boltdb-shipper storage_config: boltdb_shipper: active_index_directory: /var/loki/data/index cache_location: /var/loki/data/boltdb-cache shared_store: filesystem limits_config: retention_period: 24h write: replicas: 1 read: replicas: 1- Create the namespace
kubectl create namespace loki
- Create 2 PersistentVolumes that will be used by loki read / write components
apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolume metadata: name: loki-pv-1 namespace: loki spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce capacity: storage: 10Gi persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain local: path: [YOUR_NODE_LOCAL_STORAGE_FOLDER_1] nodeAffinity: required: nodeSelectorTerms: - matchExpressions: - key: kubernetes.io/hostname operator: In values: - [YOUR_NODE_NAME] --- apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolume metadata: name: loki-pv-2 namespace: loki spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce capacity: storage: 10Gi persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain local: path: [YOUR_NODE_LOCAL_STORAGE_FOLDER_2] nodeAffinity: required: nodeSelectorTerms: - matchExpressions: - key: kubernetes.io/hostname operator: In values: - [YOUR_NODE_NAME]- Install the helm chart
helm install --values values.yaml loki --namespace=loki grafana/loki-simple-scalable
Once all components are started up, you should have the following scenario:
[rockylinux@test-vm grafana-loki]$ kubectl get all -n loki NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/loki-gateway-55fccf8654-vcxqt 1/1 Running 0 23h pod/loki-grafana-agent-operator-684b478b77-vwh9g 1/1 Running 0 23h pod/loki-logs-wwcp5 2/2 Running 0 23h pod/loki-read-0 1/1 Running 0 32m pod/loki-write-0 1/1 Running 0 32m NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE service/loki-gateway ClusterIP 10.106.191.67 <none> 80/TCP 23h service/loki-memberlist ClusterIP None <none> 7946/TCP 23h service/loki-read ClusterIP 10.103.120.150 <none> 3100/TCP,9095/TCP 23h service/loki-read-headless ClusterIP None <none> 3100/TCP,9095/TCP 23h service/loki-write ClusterIP 10.98.226.44 <none> 3100/TCP,9095/TCP 23h service/loki-write-headless ClusterIP None <none> 3100/TCP,9095/TCP 23h NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE daemonset.apps/loki-logs 1 1 1 1 1 <none> 23h NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE deployment.apps/loki-gateway 1/1 1 1 23h deployment.apps/loki-grafana-agent-operator 1/1 1 1 23h NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE replicaset.apps/loki-gateway-55fccf8654 1 1 1 23h replicaset.apps/loki-grafana-agent-operator-684b478b77 1 1 1 23h NAME READY AGE statefulset.apps/loki-read 1/1 23h statefulset.apps/loki-write 1/1 23h
Promtail deployment
Promtail tails log files and pushed them into loki.
To deploy all required components, apply the following yaml:
--- # Daemonset.yaml apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: DaemonSet metadata: name: promtail-daemonset spec: selector: matchLabels: name: promtail template: metadata: labels: name: promtail spec: serviceAccount: promtail-serviceaccount containers: - name: promtail-container image: grafana/promtail args: - -config.file=/etc/promtail/promtail.yaml env: - name: 'HOSTNAME' # needed when using kubernetes_sd_configs valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: 'spec.nodeName' volumeMounts: - name: logs mountPath: /var/log - name: promtail-config mountPath: /etc/promtail - mountPath: /var/lib/docker/containers name: varlibdockercontainers readOnly: true volumes: - name: logs hostPath: path: /var/log - name: varlibdockercontainers hostPath: path: /var/lib/docker/containers - name: promtail-config configMap: name: promtail-config --- # Daemonset.yaml apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: DaemonSet metadata: name: promtail-daemonset spec: selector: matchLabels: name: promtail template: metadata: labels: name: promtail spec: serviceAccount: promtail-serviceaccount containers: - name: promtail-container image: grafana/promtail args: - -config.file=/etc/promtail/promtail.yaml env: - name: 'HOSTNAME' # needed when using kubernetes_sd_configs valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: 'spec.nodeName' volumeMounts: - name: logs mountPath: /var/log - name: promtail-config mountPath: /etc/promtail - mountPath: /var/lib/docker/containers name: varlibdockercontainers readOnly: true volumes: - name: logs hostPath: path: /var/log - name: varlibdockercontainers hostPath: path: /var/lib/docker/containers - name: promtail-config configMap: name: promtail-config -- # configmap.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: promtail-config data: promtail.yaml: | server: http_listen_port: 9080 grpc_listen_port: 0 clients: - url: http://loki-write.loki.svc.cluster.local:3100/loki/api/v1/push tenant_id: 1 positions: filename: /tmp/positions.yaml target_config: sync_period: 10s scrape_configs: - job_name: pod-logs kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod pipeline_stages: - docker: {} relabel_configs: - source_labels: - __meta_kubernetes_pod_node_name target_label: __host__ - action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_label_(.+) - action: replace replacement: $1 separator: / source_labels: - __meta_kubernetes_namespace - __meta_kubernetes_pod_name target_label: job --- # Daemonset.yaml apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: DaemonSet metadata: name: promtail-daemonset spec: selector: matchLabels: name: promtail template: metadata: labels: name: promtail spec: serviceAccount: promtail-serviceaccount containers: - name: promtail-container image: grafana/promtail args: - -config.file=/etc/promtail/promtail.yaml env: - name: 'HOSTNAME' # needed when using kubernetes_sd_configs valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: 'spec.nodeName' volumeMounts: - name: logs mountPath: /var/log - name: promtail-config mountPath: /etc/promtail - mountPath: /var/lib/docker/containers name: varlibdockercontainers readOnly: true volumes: - name: logs hostPath: path: /var/log - name: varlibdockercontainers hostPath: path: /var/lib/docker/containers - name: promtail-config configMap: name: promtail-config -- # configmap.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: promtail-config data: promtail.yaml: | server: http_listen_port: 9080 grpc_listen_port: 0 clients: - url: http://loki-write.loki.svc.cluster.local:3100/loki/api/v1/push tenant_id: 1 positions: filename: /tmp/positions.yaml target_config: sync_period: 10s scrape_configs: - job_name: pod-logs kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod pipeline_stages: - docker: {} relabel_configs: - source_labels: - __meta_kubernetes_pod_node_name target_label: __host__ - action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_label_(.+) - action: replace replacement: $1 separator: / source_labels: - __meta_kubernetes_namespace - __meta_kubernetes_pod_name target_label: job - action: replace source_labels: - __meta_kubernetes_namespace target_label: namespace - action: replace source_labels: - __meta_kubernetes_pod_name target_label: pod - action: replace source_labels: - __meta_kubernetes_pod_container_name target_label: container - replacement: /var/log/pods/*$1/*.log separator: / source_labels: - __meta_kubernetes_pod_uid - __meta_kubernetes_pod_container_name target_label: __path__ --- # Clusterrole.yaml apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRole metadata: name: promtail-clusterrole rules: - apiGroups: [""] resources: - nodes - services - pods verbs: - get - watch - list --- # ServiceAccount.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceAccount metadata: name: promtail-serviceaccount --- # Rolebinding.yaml apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRoleBinding metadata: name: promtail-clusterrolebinding subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: promtail-serviceaccount namespace: default roleRef: kind: ClusterRole name: promtail-clusterrole apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.ioLoki datasource configuration on Grafana admin UI
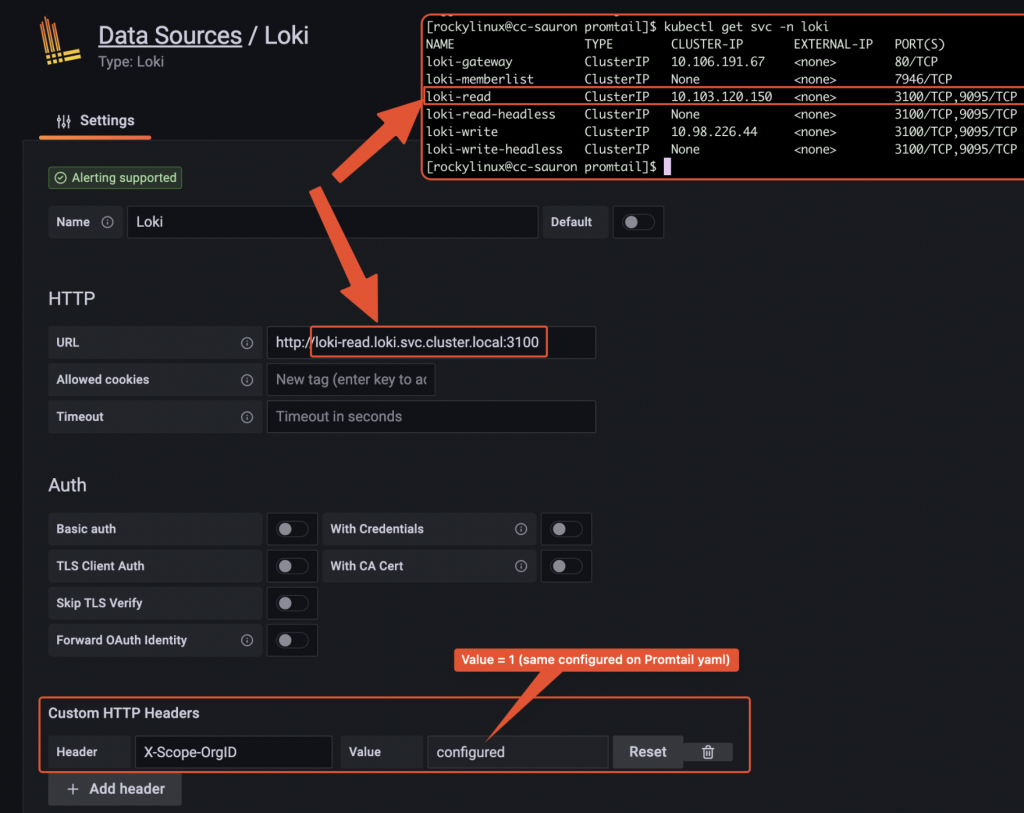
Datasource configuration on Grafana Browsing logs from Grafana UI
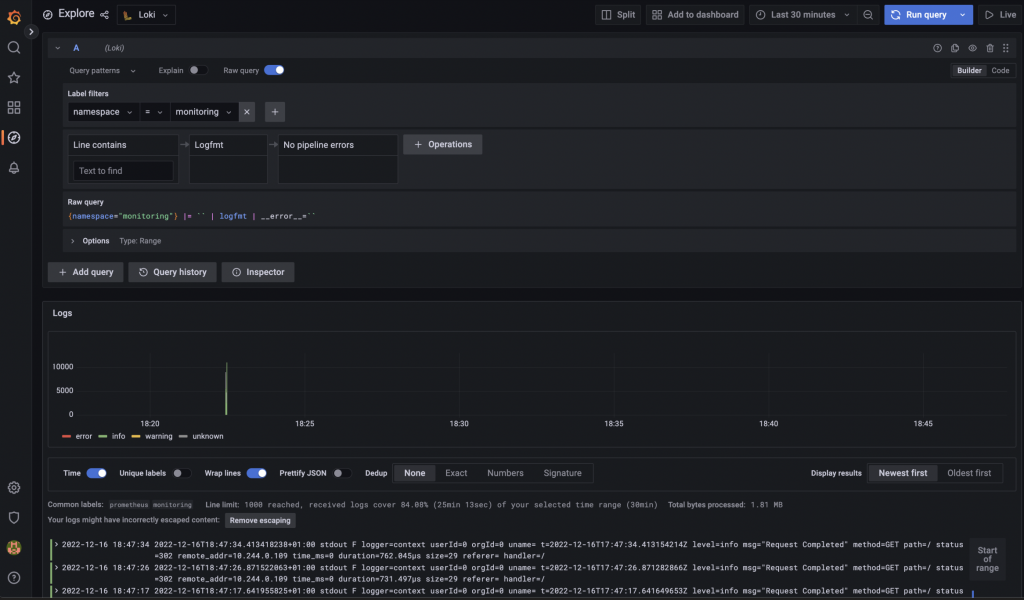
Data browser on Grafana -
Monitoring application health with blackbox-exporter
Prometheus standard deployment and configuration has already been discussed on other posts, but what if you want to expose metrics about your custom application stack health? This page explains how to achieve this, by taking advantage of blackbox-exporter, so that your application components running on a kubernetes cluster will be easily monitored.
Intro
Generally speaking, blackbox stands in between your Prometheus instance and your custom application components: Prometheus fetches metrics asking blackbox to target custom endpoints. Response will be given back using the format expected by Prometheus. Endspoints are typically your cluster’s Pods, Services and Ingresses.
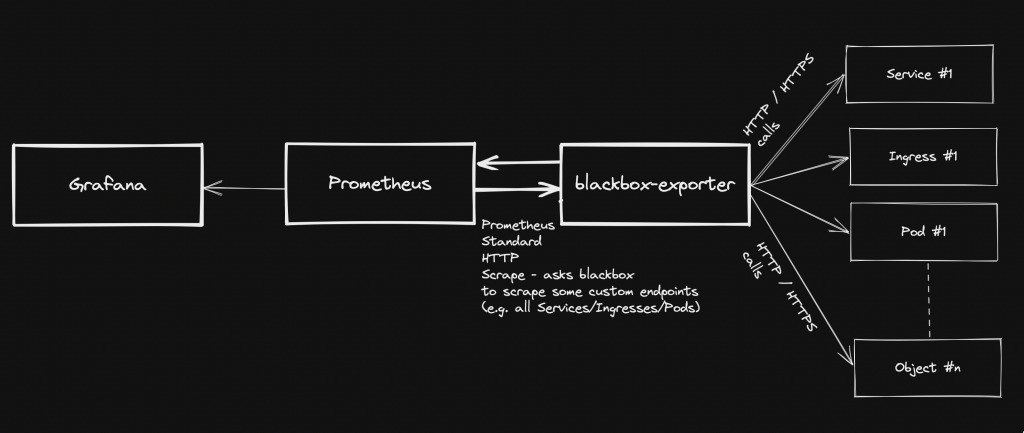
Overview Pre-requirements
- A kubernetes cluster with kubectl configured to interact with it
- Prometheus-operator stack – see https://github.com/prometheus-operator/prometheus-operator
- Grafana (part of Prometheus-operator)
blackbox-exporter installation (via helm chart)
- Add the helm repo
helm repo add prometheus-community https://prometheus-community.github.io/helm-charts help repo update
- Create a file: values.yaml
config: modules: http_2xx: prober: http timeout: 5s http: valid_http_versions: ["HTTP/1.1", "HTTP/2.0"] follow_redirects: true preferred_ip_protocol: "ip4"- Install the helm chart (in this case, we are using “monitoring” namespace):
helm install prometheus-blackbox prometheus-community/prometheus-blackbox-exporter -n monitoring -f values.yaml
Adding custom scrape targets to blackbox
As regards how to add extra scrape targets, see https://matteorenzi.com/2022/10/08/prometheus-operator-how-to-add-custom-scrape-targets/
Below some sample targets that you might want to add:
Probing external targets (sample: www.google.com)
- job_name: 'blackbox-external-targets' metrics_path: /probe params: module: [http_2xx] static_configs: - targets: - https://www.google.com relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__address__] target_label: __param_target - source_labels: [__param_target] target_label: instance - target_label: __address__ replacement: prometheus-blackbox-prometheus-blackbox-exporter.monitoring.svc.cluster.local:9115Probing your cluster Services
- job_name: "blackbox-kubernetes-services" metrics_path: /probe params: module: [http_2xx] kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: service relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__address__] target_label: __param_target - target_label: __address__ replacement: prometheus-blackbox-prometheus-blackbox-exporter.monitoring.svc.cluster.local:9115 - source_labels: [__param_target] target_label: instance - action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+) - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace] target_label: kubernetes_namespace - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name] target_label: kubernetes_service_nameProbing cluster Ingresses
- job_name: "blackbox-kubernetes-ingresses" metrics_path: /probe params: module: [http_2xx] kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: ingress relabel_configs: - source_labels: [ __meta_kubernetes_ingress_scheme, __address__, __meta_kubernetes_ingress_path, ] regex: (.+);(.+);(.+) replacement: :// target_label: __param_target - target_label: __address__ replacement: prometheus-blackbox-prometheus-blackbox-exporter.monitoring.svc.cluster.local:9115 - source_labels: [__param_target] target_label: instance - action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_ingress_label_(.+) - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace] target_label: kubernetes_namespace - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_ingress_name] target_label: ingress_nameProbing cluster Pods
- job_name: "blackbox-kubernetes-pods" metrics_path: /probe params: module: [http_2xx] kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__address__] target_label: __param_target - target_label: __address__ replacement: prometheus-blackbox-prometheus-blackbox-exporter.monitoring.svc.cluster.local:9115 - source_labels: [__param_target] replacement: /health target_label: instance - action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_label_(.+) - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace] target_label: kubernetes_namespace - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_name] target_label: kubernetes_pod_nameChecking new targets / probes
Once the new scraping targets have been applied, they must be visible on Prometheus: Status -> Targets
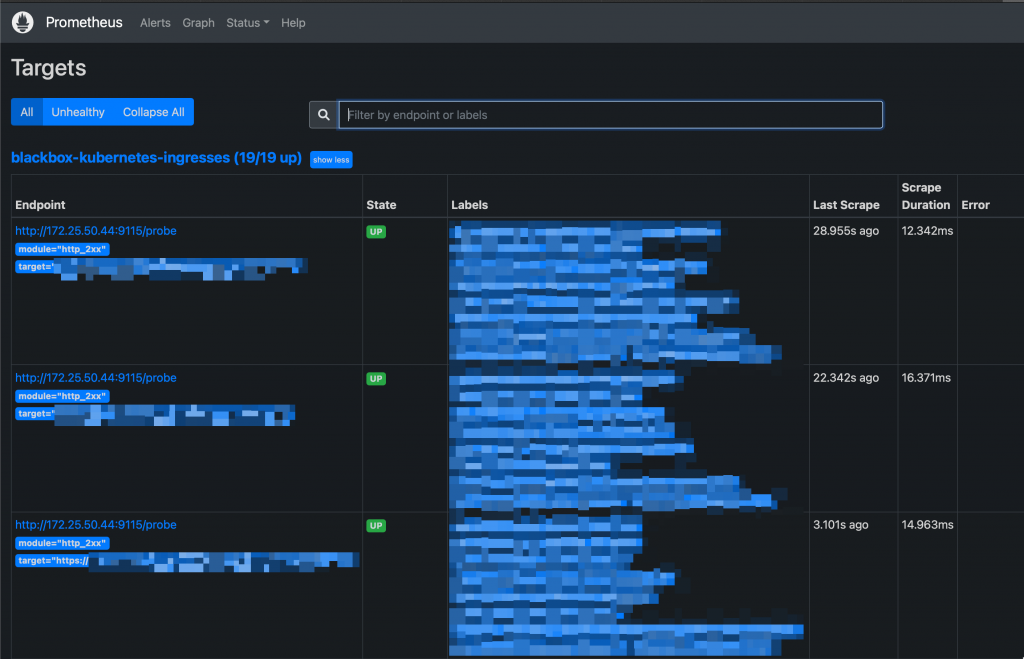
New Targets on Prometheus UI Probes can be queried like this:
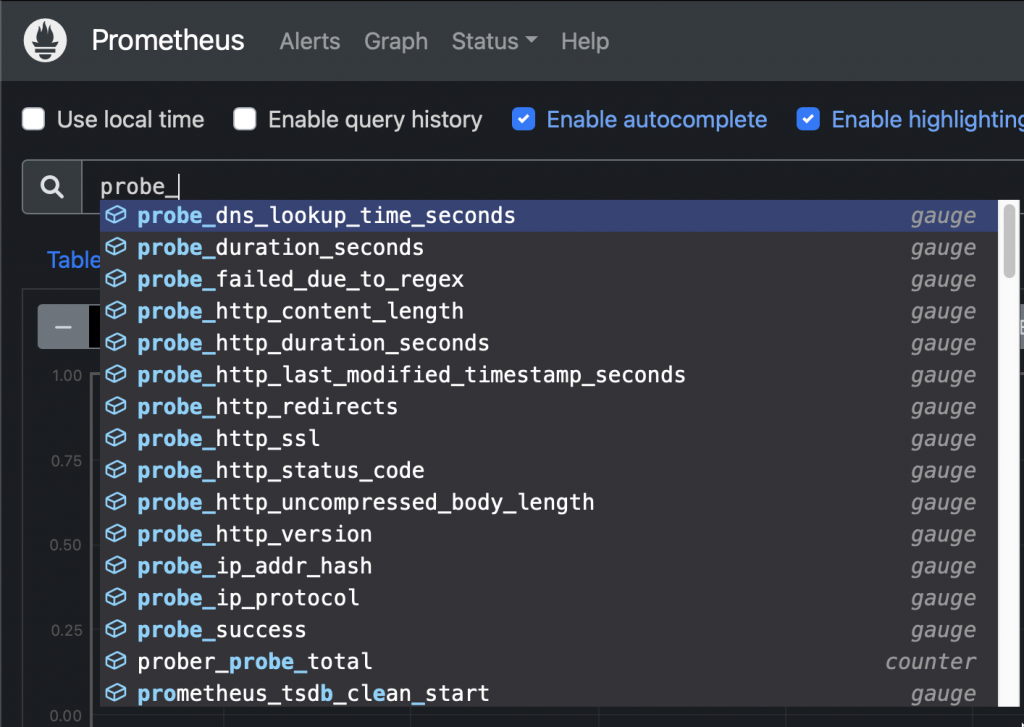
New probes Sample query: Check HTTP status code from an ingress:
probe_http_status_code{ingress_name="xxxxx"}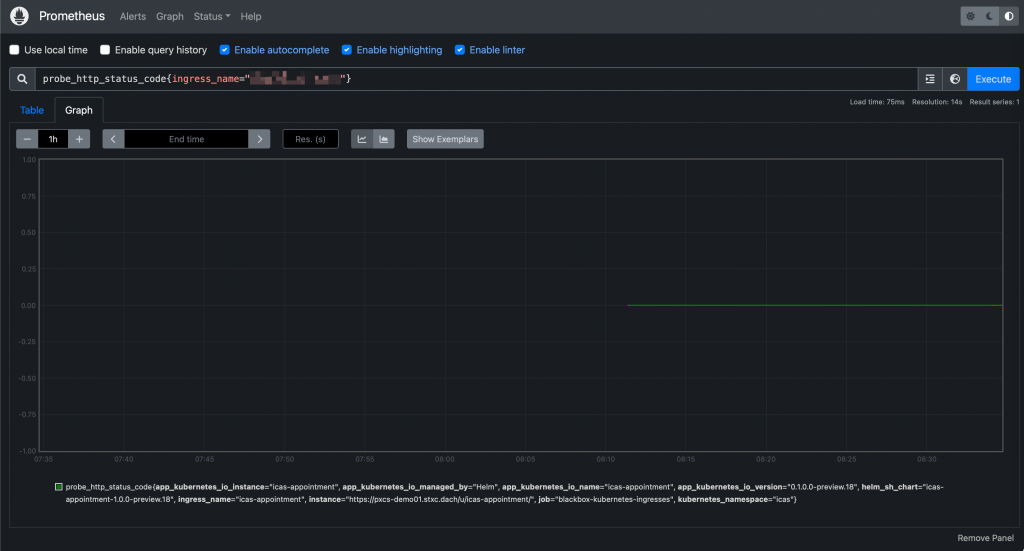
Prometheus UI: Querying a probe And they will be accessible from Grafana as well:
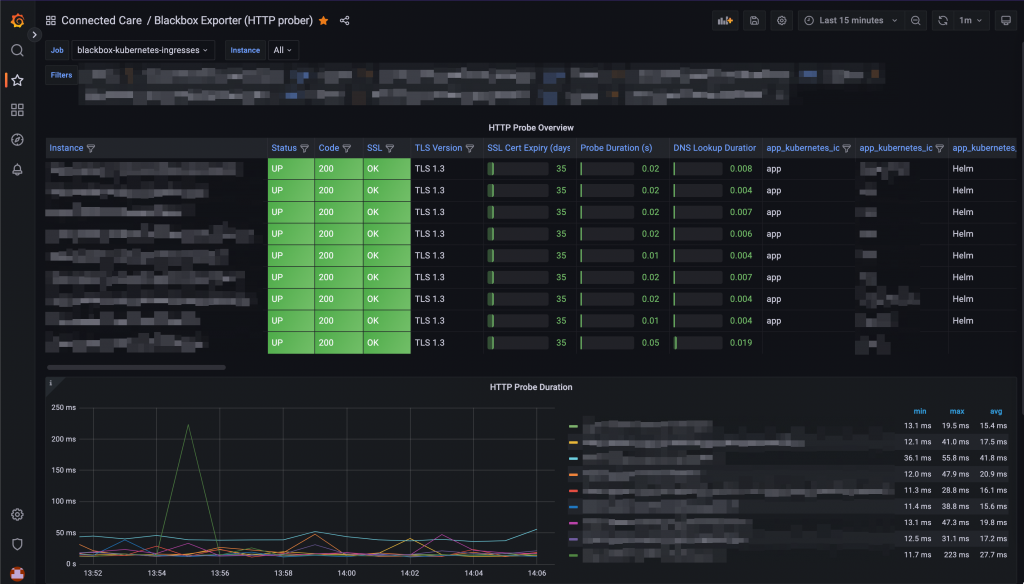
Probes visualisation on a Grafana dashboard -
Grafana running on kubernetes: How to configure SMTP integration
Grafana has a built-in alerting system and it can be used to trigger email notifications whenever an alert is raised. This page shows you how to configure the integration with an external SMTP server.
- Create a ConfigMap that includes the grafana.ini main configuration file
- Sample ConfigMap yaml manifest:
apiVersion: v1 data: grafana.ini: | [analytics] check_for_updates = true [grafana_net] url = https://grafana.net [log] mode = console [paths] data = /var/lib/grafana/ logs = /var/log/grafana plugins = /var/lib/grafana/plugins provisioning = /etc/grafana/provisioning [server] domain = [smtp] enabled = true host = smtp.test.com:587 user = test@test.com password = xxxxxxxxx startTLS_policy = MandatoryStartTLS skip_verify = true from_address = test@test.com from_name = Grafana kind: ConfigMap metadata: annotations: meta.helm.sh/release-name: prometheus meta.helm.sh/release-namespace: monitoring labels: app.kubernetes.io/instance: prometheus app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm app.kubernetes.io/name: grafana app.kubernetes.io/version: 9.1.4 helm.sh/chart: grafana-6.38.0 name: prometheus-grafana namespace: monitoring- Restart grafana pod(s) to apply the new config described above:
# kubectl delete -n monitoring $(kubectl get pods -n monitoring -o=name -l app.kubernetes.io/name=grafana)
- Create a ConfigMap that includes the grafana.ini main configuration file